The non-standard growth of skin cells is often called tumors.As the main cause of tumors, experts say the impact of ultraviolet rays.
The second cause of skin damage is carcinogens.Behind any new education on skin, it is necessary to monitor and consult doctors oncologists in a timely manner.
He will perform all necessary diagnostic procedures.He will recommend further actions you take.
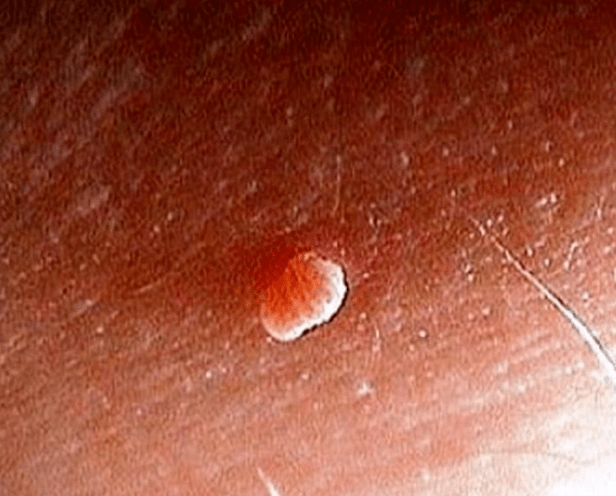
Papilloma, warts and helper tumors - all of which are the result of papillomavirus or HPV activity.The virus enters the human body and exists for a long time.HPV activation occurs under the influence of priming factors.This is formed by soft growth on the skin and mucous membranes.
Tumors are able to worsen quality of life, and their cells are characterized by softness, leading to oncology.Timely diagnosis of genitals and papilloma treatment are key to a healthy and complete intimate life for women.
Causes of papilloma in the mouth
The main reason for growth in the oral cavity is the presence of human papillomavirus in the body.They are easily infected: the virus spreads through personal contact to the family mode (touch, unprotected gender).The main methods of viral infection:
- Not complying with personal hygiene rules and using other people’s toothbrushes and towels;
- The family method includes the adverse disinfection of objects and cutlery for use with the infected person;
- Personal contact with virus carriers (kissing, oral sex, sex);
- Infection of the newborn virus occurs in the mother's birth duct along the HPV carrier's birth duct.
The incubation period of the disease may last for several years.HPV can only be found through tests.
There are many factors that affect the appearance of virus activation and symptoms:
- Frequent colds and chronic inflammatory processes lead to reduced immunity;
- stressful lifestyles and bad habits;
- Hormone violations;
- Long-term intake of antibiotics and corticosteroids (hormonal drugs);
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- Pregnant;
- Systemic damage to the oral mucosa (using toothbrushes on the chest, hot food and drinks, toothification, braces);
- Tooth caries, periodontal disease, gingivitis.
Any papilloma that appears in the body is caused only by HPV (human papillomavirus).Papillomas in intimate locations are a widespread phenomenon.Grow in the groin, vagina, member, anal area.Usually, sexual papillomas are found in children.Tumors can not only pass them to the carrier, but also cause discomfort.According to medical statistics, genital papillomavirus is found in almost one-quarter of the population.
The mechanism of papilloma formation in the intimate zone
In an inactive state, the sex virus of human papilloma can live in the body for a long time.Carriers of the virus can infect others without realizing it at all.
When the human body's protective power is weakened, the activation and growth process of viral cells occurs.Therefore, tumors occur.
With the general view that papilloma causes discomfort only in plastic surgery terms, it can also cause health problems.
Types of HPV
According to international standards, all tumors are divided into three types:
- benign.
- Malignant.
- Boundary (precancerous).
It is important to be able to determine the appearance of a papilloma in the body.The type of tumor depends on the strain of the virus.
In most cases, people face non-hazardous forms of infection that do not harm health and only cause aesthetic discomfort.Removing such warts is enough to forget the discomfort.
By comparing various photos, it is very simple to distinguish different types of warts on the body.Each type of education has many characteristics, and knowing which traits is easy to doubt the specific form of the disease.
Common papilloma or vulgar warts
The most common form of papillomavirus manifestation is common papilloma, commonly known as warts.They are caused by several strains of the virus, which are easily transmitted through contact and sexual intercourse.
According to statistics, at least every third person on Earth in his life has encountered the arrival of a common papilloma.
There are several types of papillomas in the mouth:
- Epithelial hyperplasia - small formations in papillary form, usually formed on the lateral side of the language;
- Simple (vulgar) papillomas appear in the sky, with the shape of flat cones.
- crude papilloma;
- Growth on the gums is usually expressed in the form of flat papillomas.
- Flat nipples;
- Thin-film papillomas have a delicate basis, and if injured, are usually the cause of bleeding and inflammation.Found on the bridge of the tongue;
- neblomes in the tongue;
- Sharp borum tumors have a conical shape and are interconnected, creating a huge focal point of damage.
- Sharp papilloma

Important!An inappropriate diagnosis threatens the growth of papillary lymph nodes on the respiratory mucosa.
The papillomas on the tongue and cheek may have different shapes.The polyps on the cheeks are a small soft bulge that does not cause pain.The growth of language can be affected by stimulation and micrograss, which can cause bleeding.
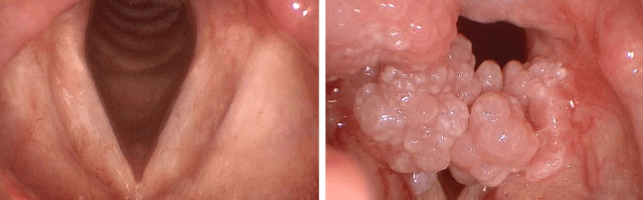
Papillomas on tonsils are often confused with laryngitis or sore throat.Due to growth, swelling of the respiratory tract and vocal cords can be observed, which can cause dyspnea.
The process of absorbing food, even liquids.Sometimes, a person experiences the presence of foreign objects in his throat.
The appearance of papillomas on the nipple may be accompanied by changes in sound and respiratory problems.During consumption of solid food, mucous membranes with growth can be crushed.A child's red throat may indicate growth.Papillomatosis in children's throat is the cause of bronchitis.
The occurrence of pathological formation on the gums (growth on the gums) in the form of cones or polyps is dangerous because the mucosa will be damaged by a toothbrush or teeth.Ultimately, this will lead to an inflammatory process and infection with non-treated sores.
In addition to skin changes, papillomavirus is also dangerous to the development of various diseases.The type of infection indicates how it will develop and what dangers it is.
It is necessary to determine the type of pore group:
- Identify whether there is a risk of regeneration into a malignant tumor.
- Select effective treatment;
- Determine the type of infection.
Simple
Also known as vulgar or ordinary.The papilloma is a slight burning feeling before it forms.
Over time, spherical growth occurs, similar to tumors.Even in the future, the smooth surface of the tumor will become rough and the color of the body will become darker.
Sizes can range from 1 to 10 mm.
Most of the time, ordinary warts appear between the fingers and the back palm.In children who are mainly moving crawling, their knees can be positioned.It's single and multiple.
Usually, vulgar papillomas do not pose a danger to human health and represent benign growth.
Asia Factory
The name itself represents the localization of papilloma.To avoid misunderstanding them with corn, there are many signs of speaking:
- The tumor on all signs resembles a common wart.
- The growing area will be painful when wearing small-sized shoes.
- There is no skin pattern and the surface is very rough.
Over time, when bubbles form nearby, plants are inherently mosaic papillomatosis - over time - papillomatosis.
In young children, plantar warts can disappear on their own.
Flat
Their oval, stretched, less circular shapes.They are characterized by slightly higher heights - only a few millimeters protruding above the skin.The face is affected, the skin on the upper part of the chest, and sometimes external reproductive organs.
The color is slightly darker than the body.Nearby, aircraft papillomas have the property of connecting to a location, after which they become more pronounced.
Movie
Warts characterized by specific leg and longitudinal shapes are called threads (Acrochordus).Initially, the tumor at the bottom takes the form of a small cone, which stretches quickly.
40 years later, it is most often found in men and women.They are located on the neck, eyelids, underarms, groin areas, near the breast.Often injured due to thin legs, clothes are prone to damage or incorrect movement.
Sharp
External similarity to nipple education.They can affect the skin throughout the group and throughout the group.As they develop, they combine into a whole to form the flesh of a comb or a bright pink.
Acneal warts are caused by sexually transmitted infections.In this regard, assistive tumors affect genitals, groin areas, and areas near the anus.
Sharp papillomas develop quickly and can occupy most of healthy tissue in a few days.Even after successful treatment, recurrence was not ruled out.
There are more than one hundred papillomaviruses in medicine.About 40 of them are sexually transmitted, thus affecting the genitals of men and women. Many types of HPV do not harm at all, and some are particularly dangerous and can cause tumor diseases.
Types of human papillomavirus are habitually classified according to the probability of carcinogenic formation on the skin.distinguish:
- A particularly dangerous type - 16, 18, 36, 45;
- The types of average hazards are 31, 33, 35, 51, 52, 58;
- Security types - 6, 11, 42, 43, 44.
HPV is a microorganism with up to a hundred stamps.Different types of papillomas have also formed on the skin according to the type of people affecting HPV stamps.Their appearance, growth rate, and location in the body are different.
Some papillary growth was detected in the mucosa of the mouth, the bladder, the female in the vagina, and the male in the penis.
Identifying papilloma species is necessary to select the most effective treatment and assess the risk of regeneration of the tumor into a malignant tumor.
Official medicine divides HPV into 4 groups:
- non-structural;
- Low carcinogenicity;
- Take on average risk of cancer;
- It has high carcinogenic characteristics.
Usually, over time, non-rehabilitative is not reborn as cancer, and is a vulgar, flat, sole-type papilloma.If we take the general definition of papilloma, then translate from Latin, you can describe it as a "tumor in a papillary form".















